While they have always played a pivotal role in business success, the terms ‘data report’ or ‘business report’ haven’t exactly been synonymous with creativity or innovation. Data reporting is often seen as a necessary evil created by analysts and consultants to offer functional operational insights. As such, the term usually conjures up images of static PDFs, old-school PowerPoint slides, and big tables. Usually created with past data without any room for generating real-time or predictive insights, data reports were deemed obsolete, consisting of numerous external and internal files, without proper data management processes at hand.
But in the digital age, it doesn’t have to be this way. In fact, the business intelligence industry has evolved enormously over the past decade, and data reports are riding the crest of this incredible technological wave.
The rise of innovative report tools means you can create report data that people are compelled to read and that will offer a wealth of business-boosting value. If you utilize business intelligence correctly, not only you will be able to connect your data dots, but take control of your data across the company and improve your bottom line.
Here, we will consider the question, ‘what is a data report?’, explore how to arrange report data, and provide the best possible data reports examples, all created with modern software. Without further ado, read on to see why data reports matter and our top data reporting tips.
What Is a Data Report?
A data report is an evaluation tool used to assess past, present, and future business information while keeping track of the overall performance of a company. It combines various business data and usually used both on an operational or strategic level of decision-making.
As mentioned, these reports had features of static presentation of data, manually written or calculated, but with the introduction of modern processes such as dashboard reporting, they have developed into an invaluable resource to successfully manage your sales processes, marketing data, even robust manufacturing analytics and numerous other business processes needed to stay on top of the pack.
But let’s get into the basics in more detail, and afterward, we will explore data reporting examples that you can use for your own internal processes and more.
Data Reporting Basics
We’ve explored the data reports definition – now, it’s time to look at the essential reports and data fundamentals: the building blocks of business intelligence success.
- Purpose: Data analytics is the art of curating and analyzing raw data with the purpose of transforming metrics into actionable insight. Data reports present metrics, analyses, conclusions, and recommendations in an accessible, digestible visual format so everyone in an organization can make informed data-driven decisions.
- Data types: Business data reports cover a variety of topics and organizational functions. As such, all data report types vary greatly in length, content, and format. It’s possible to present reporting data as an annual report, monthly sales report, accounting report, reports requested by management exploring a specific issue, reports requested by the government showing a company’s compliance with regulations, progress reports, feasibility studies, and more. The all-encompassing nature of data-centric reports means that it’s possible to work with a mix of historic, predictive, and real-time insights to paint a panoramic picture of your organization’s functions, processes, and overall progress.
- Accessibility: Historically, creating business data reports was time- and resource-intensive. Data pull requests were the exclusive duties of the IT department, with a significant amount of time spent analyzing, formatting, and then presenting the data. Because this task was so resource-heavy, data analysis was an occasional luxury. Also, by the time the data was presented, it was generally out of date. The emergence of real-time cloud-based BI reporting tools has changed the data reporting game. Now a wider range of business users can act as analysts, even performing advanced analytics. The right BI platform can blend multiple data sources into one report and analysis: enhancing business insights and better-informed decision making. These cloud-based tools allow organizations to collaborate on a report, bringing various subject matter experts (SME) to the same table. Modern business dashboard tools allow a wider audience to comprehend and disseminate the report findings. Users can also easily export these dashboards and data visualizations into visually stunning reports that can be shared via multiple options such as automating emails or providing a secure viewer area, even embedding reports into your own application, for example.
- Flexibility: In addition to the fact that data report software offers a wealth of visually-accessible KPI-driven insight, business intelligence dashboards are also completely customizable to suit individual business goals or needs. Moreover, data dashboards are optimized for mobile devices, meaning that it’s possible for users to access a wealth of business-boosting information from a central dashboard, 24/7, without restrictions or limits. You can leverage business intelligence at any time of day or night, from anywhere in the world.
Now that you understand the superior analytical capabilities of modern business data reporting, we’re going to look at a mix of tips and ideas designed to help you build and create data reports that will save time and costs while driving innovation across the business.
“The future belongs to those who see possibilities before they become obvious.” – John Sculley, early adopter, and advocate of data intelligence
How to Write a Data Report

We’ve been through the basics, so now, it’s time to look at how to create data reports from a practical perspective. That’s where our documenting data in business reports tips come into play.
Depending on the type of the report, each has its own set of rules and best practices. We will mention below the most popular ones, but our main focus is on business data reports that will, ultimately, provide you with a roadmap on how you can make your reports more productive. Let’s get started.
1. Define The Type Of Your Data Report
What types of data reporting do you need to present? Having this definition ahead of time will help set parameters you can easily stick to. Here are the most common data report types:
1) Informational vs. analytical: First determine if this report is just providing factual information. Informational reports are usually smaller in size, the writing structure is not strict, and the sole purpose is to inform about facts without adding any analysis. On the other hand, if it is providing any analysis, demonstrates relationships or recommendations, it is an analytical report.
2) Recommendation/justification report: Presents an idea and makes suggestions to management or other important decision-makers. What the name suggests, it provides recommendations to changes in business procedures and justifies courses of actions that have the goal of improving business performance.
3) Investigative report: Helps determine the risks involved with a specific course of action. Here, reporting data is based on documenting specific information objectively with the purpose of presenting enough information to stakeholders. They will ultimately decide if further actions are needed. An example would be a report created for legal purposes.
4) Compliance report: Shows accountability by providing compliance information for example to a governing body. This is particularly important as accurate, well presented compliance data will avoid costly mistakes or red tape issues.
5) Feasibility report: An exploratory report to determine whether an idea will work. Data-driven insights that could potential save thousands of pounds by helping businesses avoid redundant processes or developments.
6) Research studies report: Presents in-depth research and insights on a specific issue or problem. Research is pivotal to growth and evolution and having the visual data to back up your decisions will set you apart from the pack.
7) Periodic report: Improves policies, products or processes via consistent monitoring at fixed intervals, such as weekly, monthly, quarterly, etc. These types of reports help foster incremental growth as well as consistency across the board.
8) KPI report: Monitors and measures key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess if your operations deliver the expected results. The best dashboards for benchmarking progress in a number of areas, both internal and external.
9) Yardstick report: Weighs several potential solutions for a given situation. An invaluable tool that you can adapt to your specific goals, aims, needs, and situations. A solution-centric tools that every modern business should embrace.
2. Know Your Target Audience
Knowing your audience will help determine what data you present, the recommendations you make and how you present the data. Your audience may be upper, middle or line management, other departments in the company, coworkers, the client, potential clients, the government or another company in the same market.
Knowing your audience helps determine what type of information to include in the report. If a report is internal facing, branding such as colors, font, and logo aren’t as crucial. If it is a one-time live presentation, formatting for printing isn’t key. Determine ahead of time if your audience needs persuasion or education. If your audience is C-suite level or the board, you may want to present mostly high-level data with specific call outs and action items.
If the report is more exploratory in nature, you may want to include more granular data and options to interact with the data. Ramon Ray, tech evangelist and founder of Smart Hustle Magazine, wrote about how to best present your data to a wide audience. He focused on keeping text simple, use visualizations whenever possible, including video and animation when appropriate, and making your reports/presentations interactive. Knowing your audience before you start your analysis – and even more importantly before you put together the report – will keep your reports and data focused and impactful.
3. Have A Detailed Plan And Select Your KPIs
We are going to sound like a broken record here, but have a report plan before you start your analysis. What information does the management need for its effective decision making? What data and insights do your shareholders require? Understand the scope of data required and think about how you will want to use that data.
Utilize as many data sources as possible. But don’t go data crazy and get bogged down in unnecessary information. Of course, you have to remain agile and may have to adapt the plan, but a robust plan is crucial. Remaining purpose-driven will focus your work, save you time in the long run and improve your business reporting outcomes.
When creating your plan, it is crucial to select the right key performance indicators (KPIs). You don’t need dozens of metrics that will answer all your business questions at once, but pick a few that will tell a comprehensive data story (more on that later), and enable you to take proper action (more on that later, too).
Depending on your department or industry, reports will vary as KPIs also vary, but choose the ones that will help you put your data into proper context and always keep in mind the audience you’re addressing. If you understand your audience on a deep level and set clearcut strategic objectives, you will find the KPI selection process easier and more valuable.
Choose KPIs that align directly with your specific business aims, and you will benefit from a cohesive mix of visual benchmarks that will help you track your progress accurately while spotting trends that will help you streamline your business for success.
4. Be Objective, When Possible
A good business data report describes the past, present, or possible future situation in an objective and neutral way. Objective means the report states facts, not an opinion. Keep the opinions minimal. It helps to combine them in one section, possibly titled “Suggested Actions.” Also, using a passive voice in a report will help keep the report formal and objective. For example:
Active: The managers need to make changes in their management style.
Passive: Changes in management style need to be made.
If you’re too subjective or biased with any data report format, you’re essentially moving away from your goal of uncovering factual insights that will give you a competitive edge. Collect data from reliable sources, record your insights with pinpoint accuracy, and you will connect with objective insights that will push your business to the next level.
5. Be Visually Stunning
Numerous types of data visualization have proven to be extremely powerful. Analytics presented visually make it easier for decision-makers to grasp difficult concepts or identify new patterns. Data presented visually are easier for humans to perceive and digest. Reports should include data visualizations over text whenever possible. Just make sure you are choosing the most appropriate data visualization to tell your data story and that you are following BI dashboard best practices. With the right data reporting tool, anyone can create meaningful visuals and share them with their team, customers, and other shareholders. All this can be accomplished without involving a data scientist.
Also, make sure your report remains visually stunning, no matter how it is shared and disseminated. Your report should look good on a computer, tablet, PDF, or even on a mobile screen. That’s why utilizing a dashboard can be the most cost-effective solution that will provide you with not only stunning visuals but interactivity as well.
Bonus tip: For reports like annual reports that will be printed and widely shared, the extra focus should be spent on dashboard design principles.
6. Have Content Sharply Written
While the focus should be on visuals, some data report types also need text. Make sure your reports use persuasive and even-toned business writing. Use concise, active, and engaging language. Use bullet points versus long paragraphs. Use headers and provide legends and supplementary text for your visualizations. Also, you should always proofread!
To optimize your data analytics presentation and content, our guide to digital dashboard creation and best practices offers practical insights that will help you format your reports for success.
7. Make Sure the Report Is Actionable
Prescriptive, descriptive, and predictive analytics are becoming increasingly popular in recent years. Each brings new insights needed to make better business decisions and increase ROI – insights from the past, future, and prescribing possible outcomes. That being said, make sure your report has a conclusion. When necessary, provide recommendations.
Reports should be objective but the best ones are also actionable. Intended audiences should walk away with the next steps or greater insights. By doing so, you will enable a data-driven business environment and foster a more efficient collaboration.
To help make your data-centric reports more actionable, you must ensure that your KPIs and insights work together to paint a comprehensive picture of a particular process, strategy, or function.
For instance, if you’re looking to analyze your customer service success, adding metrics relating to both staff performance and consumer satisfaction will give you a balanced mix of insights that will help you take decisive action. Naturally, all of your KPIs will offer invaluable standalone information, but if they all complement one another, you will accelerate your business success in a number of key areas.
8. Keep It Simple And Don’t Be Misleading
While data should be objective, formatting, filtering, and manipulation can be easily part of misleading statistics. Make sure you are being consistent and reliable with your reporting. Also, keep it simple. The boom of data visualization and reporting tools has led to the creation of visualizations that don’t tell a data story.
You shouldn’t need 3-D glasses to read a report. Sometimes, a simple chart is all you need. You also don’t need to go nuts with colors and formats. You can easily overwhelm your audience this way. Choose a couple of colors that are easy on the eyes. Keep to one font. Don’t go crazy with highlighted, bold or italicized text. You don’t have to create a “piece of art” for your report to be visually stunning and impactful.
The key takeaway here is: Keep your eyes on the prize and always remember the goal or primary objective when developing your reports. Remaining true to your objectives while prioritizing making your dashboards universally accessible will ensure you keep your reports simple, transparent, and accurate at all times.
9. Don’t Forget to Tell a Complete Story
To successfully report data, you must take into account the logic of your story. The report should be able to provide a clear narrative that will not confuse the recipient but enable him/her to derive the most important findings.
Consider creating a dashboard presentation. That way you will have your data on a single screen with the possibility to interact with numerous charts and graphs while your story will stay focused and effective. By utilizing interactive visualizations, you not only have a strong backbone on how to write a data report but also ensure that your audience is well-informed and digests data easily and quickly.
Human beings absorb and engage with narratives better than other formats. If you tell a tale with your data, you will skyrocket your business success, improve your chances of executive buy-in, and foster innovation across the organization.
Our definitive guide to dashboard presentation and storytelling will tell you all you need to know to get started.
10. Use Professional Data Report Software
Last but not least, utilizing a modern visual analytics software will ensure you design your reports based on the decisions you need to make, filtering the ever-present noise in reporting processes and making sure you don’t get lost in the details. Often times, reports are piled with large volumes of spreadsheets and presentation slides that can create an obscure view of the presented data, and increase the possibility of (unintentional) errors. The software can eliminate hideous manual tasks of searching through rows and columns, provide the necessary real-time view, alongside the possibility to look into the past and the future of how the data will behave.
No matter if you’re an analyst working with databases and need a strong MySQL reporting tool or a marketing professional looking to consolidate all your channels under the same data-umbrella, the software will enable you to clear the clutter and automate your reports based on your specific time intervals. They will update the data automatically, and you will not need more than small refinements to make sure the data you present is the one your audience needs.
We have expounded on the data reports definition, saw the top 10 best practices to create your own, and now we will continue our focus on data reports examples from a few industries that will present these practices in action.
Data Reports Examples and Templates
To put everything we’ve discussed so far into perspective, let’s move onto data reporting examples. To be able to create reports that drive action and provide added value to your company’s business efforts, here are some examples that put the reporting creation and presentation in perspective. These examples are created with the help of a professional dashboard designer that empowers everyone in the line of business to build their own reports. Let’s start with the finance department.
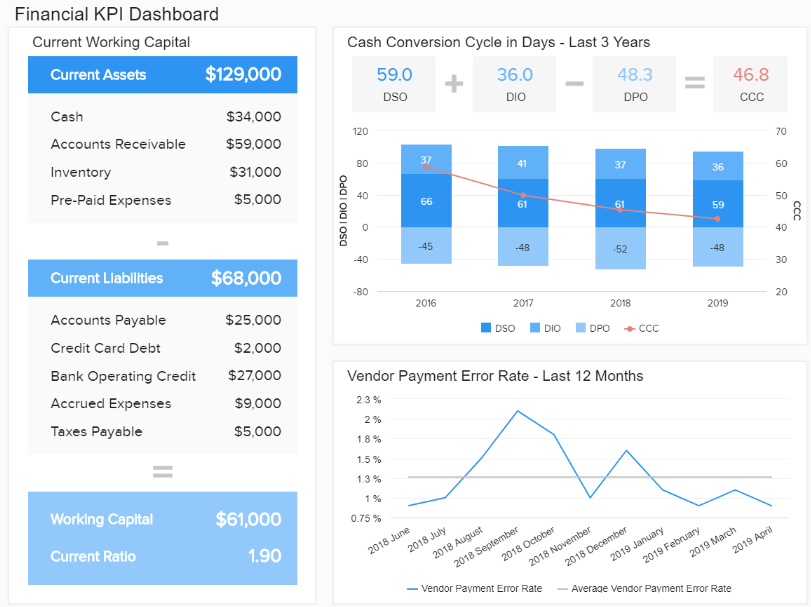
1. Financial KPI dashboard
Finance is the beating heart of any business and creating a financial report is the basis for sustainable development. Companies need to keep a close eye on how their monetary operations perform and make sure their financial data is 100% accurate.
Our example focuses on KPIs that are meticulously chosen to depict the general financial health of a company. The displayed information is presented in a logical order, connecting various financial KPIs that make a complete data story, without the need to overcrowd the screen or complicate the report.
**click to enlarge**
Primary KPIs:
- Working Capital
- Quick Ratio / Acid Test
- Cash Conversion Cycle
- Vendor Payment Error Rate
- Budget Variance
What is data reporting doing in this case is quite simple. Presenting the most important information in a clear financial narrative that will drive action. We can see in this financial dashboard that the company managed to decrease the cash cycle, but the vendor payment rate had a spike in September last year. It might make sense to take action and see in more detail what happened so that the processes can be adjusted accordingly.
2. Retail KPI dashboard
Retailers must be extra careful in picking the right KPIs and presenting their data in a clear order, without cluttering the report or confusing the people that need to read it and act accordingly.
**click to enlarge**
Primary KPIs:
- Back Order Rate
- Rate of Return
- Customer Retention
- Total Volume of Sales
A retail dashboard such as the one presented above focuses on the perspective of orders which is one of the crucial points in this cutthroat business.
Gaining access to these business touchpoints will equip you with the best possible ingredients to stay competitive on the market. By utilizing KPIs such as the rate of return (also by category), customer retention rate, and the number of new and returning customers will enable you to access in-depth information on your order processes and ensure your actions stay focused on developing your business on a sustainable level. For example, you can keep an eye on the rate of return and make sure it stays as low as possible. That way, your costs will be significantly lower and, ultimately, customers more satisfied.
Your retail analytics processes don’t need to foster complex reports, but with an example such as we presented above, you can see that reporting with dynamic visualizations empowers you to make better business decisions.
3. Talent management dashboard
The next of our data report examples is our HR dashboard focused on talent management. Talent retention and development is an ongoing challenge for HR managers. This data-centric reporting tool is designed to keep your top-performing staff engaged and motivated on a consistent basis.
**click to enlarge**
Primary KPIs:
- Talent Satisfaction
- Talent Rating
- Talent Turnover Rate
- Dismissal Rate
With a wealth of at-a-glance insights that are essential to successful talent management strategies and HR KPIs focused on the likes of rising talent as well as dismissal and turnover rates, this invaluable tool will prove vital to the health and growth of your organization. Moreover, your HR analytics efforts will prove to enhance hiring processes, enabling you to attract the best possible talent, automate tasks, and create a satisfying workforce environment.
4. Procurement quality dashboard
Our procurement dashboard is designed to streamline and fortify the relationship between you, your vendors, and your suppliers.
**click to enlarge**
Primary KPIs:
- Supplier Quality Rating
- Vendor Rejection Rate & Costs
- Emergency Purchase Ratio
- Purchases In Time & Budget
- Spend Under Management
Cohesive procurement is vital to the financial and operational success of any modern organization, regardless of industry or sector. This interactive procurement report will help you quality-check your suppliers while digging deeper into metrics surrounding emergency purchases, rejection rates, costs, budgetary constraints, and more. A business-boosting tool that will form the backbone of your business.
5. Sales opportunity dashboard
Sales are integral to the success of most businesses. Our sales dashboard will help you identify revenue-boosting sources with ease while prioritizing them in order of prospective value.
**click to enlarge**
Primary KPIs:
- Number of Sales Opportunities
- Sales Opportunity Score
- Average Purchase Value
This will allow you to streamline your sales strategy for maximum income, efficiency, and sustainability. This visually-balanced performance dashboard is easy to understand and will help you take direct action at the times when it matters most – a priceless business intelligence tool for any forward-thinking organization.
Start Building Your Data Reports Now!
Now that you know how to write a data report, it’s time to embrace the power of modern BI solutions and data analytics.
Reporting, analytics, and smart informational processing can have a transformational impact on an organization if approached the right way.
Fortunately, the mind-numbing task of manually creating daily or weekly reports is a thing of the past. With the right plan and proper business reporting software, you can easily analyze your data and also create eye-catching and remarkable reports.
We are living in the age of information – a time where anything is possible. By embracing data-centric reports and forming the right foundations, you will accelerate the success of your organization in ways you never thought possible, pushing you ahead of the pack in the process.
All you need to do is follow these essential steps and recommendations, and you will be on your way to a brighter, more prosperous commercial future. If you want to start creating your own powerful and modern reports and testing all of these practices, you can try datapine for a 14-day trial, completely free. The time to strike is now.
The post How To Create Data Reports That Will Skyrocket Your Business Performance appeared first on BI Blog | Data Visualization & Analytics Blog | datapine.